Dental
Home >> Dental
The Importance of Dental Professionals in the Fight Against Oral Cancer
Oral cancer is a serious and often overlooked disease. Early detection is crucial for successful treatment and survival. Dental professionals play a vital role in the fight against oral cancer, acting as the first line of defense in identifying suspicious lesions and ensuring timely referrals for diagnosis and treatment. This page will explore the critical role dentists play, illustrate what oral cancer can look like, explain why screening is so effective, detail the screening process, and discuss important pre-treatment dental considerations.
The Role of the Dental Profession
Dental professionals also play a crucial role in educating patients about risk factors, promoting self-examination, and encouraging regular checkups.
Dentists are often the first healthcare professionals to see patients regularly, making them crucial in detecting oral cancer in its early, more treatable stages.
They conduct comprehensive examinations of the entire oral cavity, including the tongue, gums, cheeks, floor and roof of the mouth, and oropharynx, looking for abnormalities.
Dentists are trained to recognize visual signs of oral cancer, such as unusual sores, lumps, white or red patches, or changes in tissue texture.
Dentists inquire about patients' medical history and lifestyle habits, including tobacco and alcohol use, which are major risk factors for oral cancer.
They educate patients about oral cancer risk factors, signs and symptoms, and the importance of regular self-exams.
When a suspicious lesion is found, dentists make timely referrals to specialists for further diagnosis and treatment, ensuring prompt intervention.
They use palpation (feeling with their fingers) to detect any hidden lumps or swelling in the mouth, neck, and lymph nodes.
Dentists play a vital role in addressing pre-existing dental issues before cancer treatment begins, minimizing potential complications from therapies like radiation or chemotherapy.
After cancer treatment, dentists continue to monitor patients for recurrence and manage any oral health side effects from the treatment.
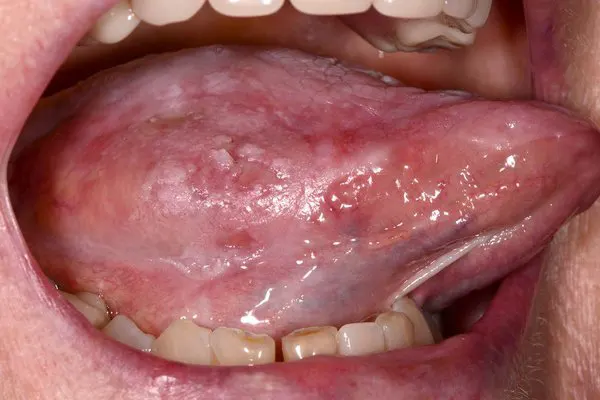
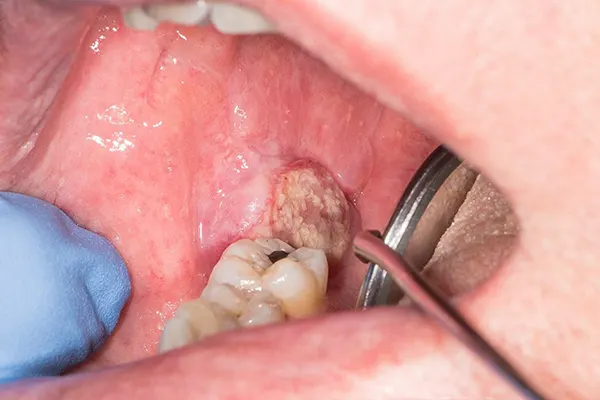
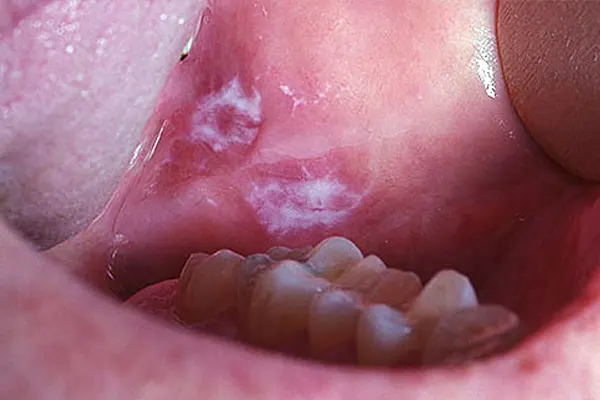
Pictures of mouth cancer
These photos give you an idea of what possible mouth cancers can look like, but remember that they might appear differently to this.
It's important to be aware of the symptoms of mouth cancer so you can contact your GP or dentist if you notice anything abnormal.
Why Screening Works
Oral cancer screening works because it allows for early detection. When oral cancer is caught in its earliest stages, the chances of successful treatment and long-term survival are significantly higher. Early-stage cancers are often smaller and less likely to have spread to other parts of the body. Screening increases the likelihood of identifying these early-stage cancers, dramatically improving patient outcomes. Regular screenings, combined with patient self-examination, are the most effective way to combat oral cancer.
Screening by Dental Professionals
The oral cancer screening process performed by dental professionals is quick, painless, and thorough. It typically involves:
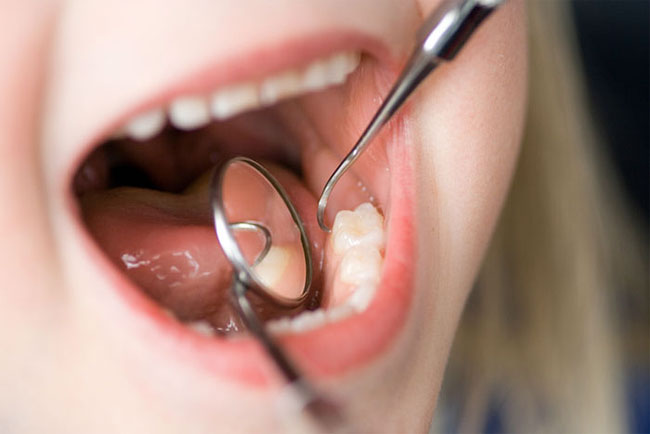
Visual Examination
The dentist or hygienist will carefully examine your mouth, looking for any abnormalities such as sores, lumps, or changes in color.
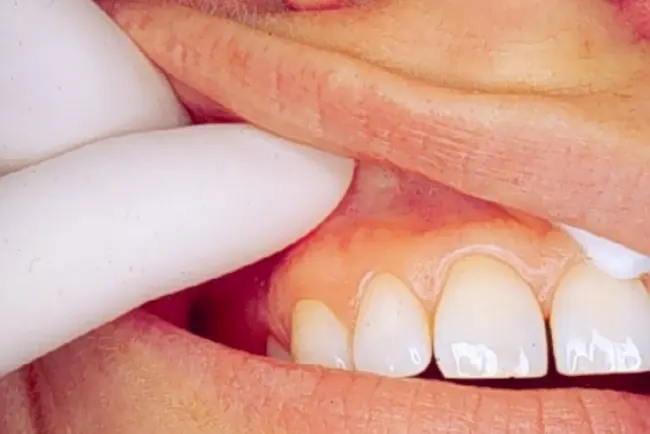
Palpation
They will gently feel the tissues in your mouth and neck to check for any unusual lumps or swelling.
Discussion of Medical History
They may ask about your medical history, including any risk factors for oral cancer, such as tobacco use, alcohol consumption, or HPV infection.
If the dentist finds anything suspicious, they may recommend further tests, such as a biopsy, to confirm a diagnosis. Early detection through professional screening is paramount for effective treatment.
Pre-treatment Dental Issues
Before beginning treatment for oral cancer, it's essential to address any existing dental issues. Radiation therapy and chemotherapy can have significant side effects on oral health, including dry mouth, mucositis (inflammation of the mouth lining), and increased risk of cavities. Addressing pre-existing dental problems, such as cavities, gum disease, or broken teeth, can help minimize these side effects and improve oral health during and after cancer treatment. A thorough dental evaluation and treatment plan before cancer therapy begins is a crucial part of comprehensive cancer care. This proactive approach helps to maintain oral health, prevent complications, and improve the patient's overall quality of life. Patients should discuss their oral health concerns with their oncologist and dentist to ensure coordinated and comprehensive care.